Random Crop
If you have ever worked on a Computer Vision project, you might know that using augmentations to diversify the dataset is the best practice. On this page, we will:
- Сover the Random Crop augmentation;
- Check out its parameters;
- See how Random Crop affects an image;
- And check out how to work with Random Crop using Python through the Albumentations library.
Let's jump in.
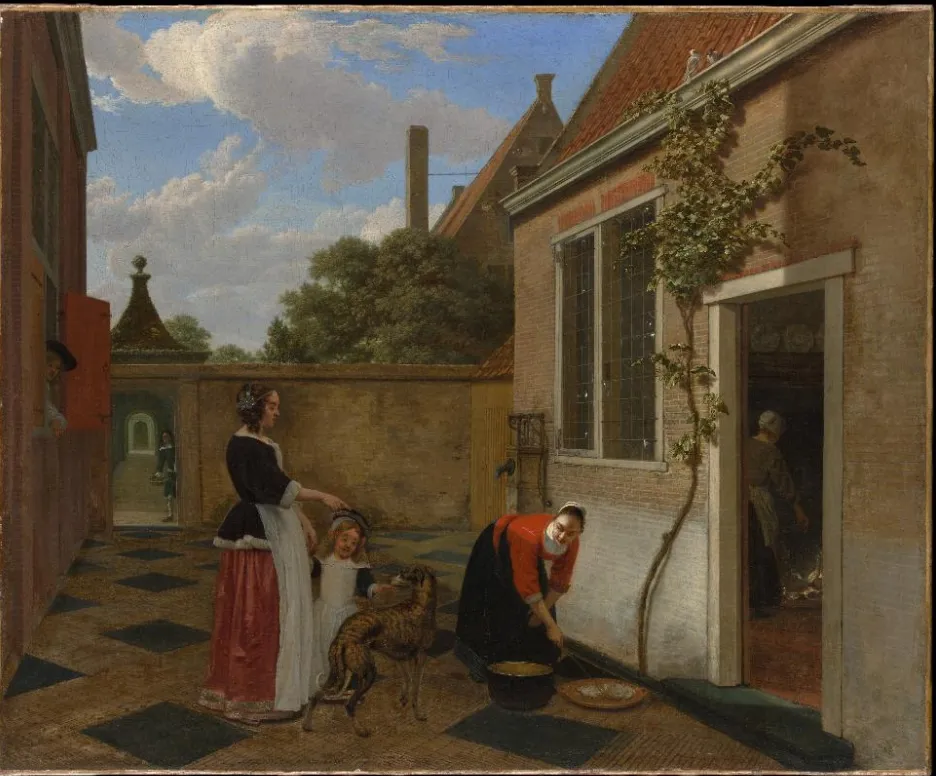
Random Crop augmentation explained
To define the term, Random Crop is a data augmentation technique that helps researchers to crop the images into a particular dimension, creating synthetic data. The cropping could result in any patch of the image and is therefore called "Random Crop."
Random Crop augmentation parameters
- Height - sets the height of the desired cropped image in pixels;
- Width - sets the width of the desired cropped image in pixels.
Random Crop augmentation visualized

Source
Source
